MAROONS
Maroons were Africans who had escaped from slavery in the Americas, mixed with the Native Americans, and formed independent settlements. Between 1780 and 1784, a group of Maroons led by Jean Saint Malo resisted re-enslavement from their base in the swamps east of New Orleans. When captured, St. Malo was hanged in Jackson Square.
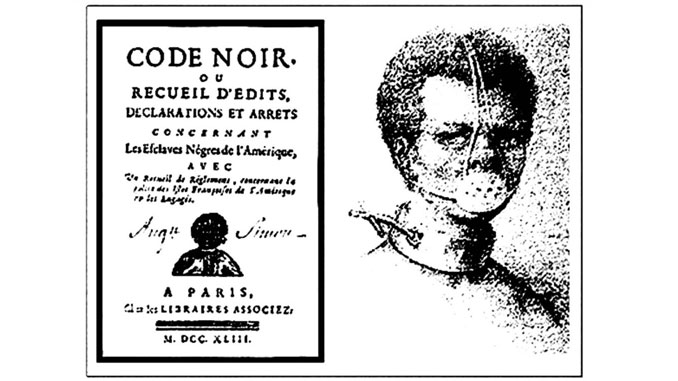
FRENCH CODE NOIR
In 1724 France imposed a set of laws called the Code Noir (Black Code) to control the lives of colonists and Africans in Louisiana. The Code Noir resulted in a far higher percentage of Blacks being free people of color (13.2%) in Louisiana compared to 0.8% in other areas. They were on average exceptionally literate, with a significant number of them owning businesses, properties, and even slaves.
NATCHEZ REVOLT
Maroon villages were centers of trade and marriage between Enslaved people and native tribes. In 1729 the powerful Natchez Indians and their Maroon allies massacred French plantation owners and liberated hundreds of slaves in an attempt to force the French out of their land. French authorities created a military force of Choctaw and Enslaved Blacks who eventually conquered the Natchez and recaptured the freed slaves.
SPANISH ARRIVE
The 1764 arrival of Antonio de Ulloa, the first Spanish Governor of Louisiana, led to the demise of the French Code Noir replacing it with a Spanish model regulating Black-White relations. Ulloa upset the French Creole Community of New Orleans when he permitted the marriage of a White Spaniard and a Black Slave. The new governor also perturbed the local White population when he restricted the common practice of whipping slaves in the City of New Orleans because the cries of whipping victims bothered his wife.
SPANISH CHANGES
A French Creole attempt to overturn Spanish Rule failed and a new Spanish Governor banned the trade of Native American slaves, although there was no movement toward abolition of the African slave trade, Spanish Rule introduced a new law called “coartación,” which allowed slaves to buy their freedom and that of other slaves.
Recommended For You.



Be the first to comment